21st February 2026
The desert and the parched land will be glad; the wilderness will rejoice and blossom like the crocus Isaiah 35:1
You Lord, are the source of all good things:
We praise you.
You call us to tend and care for your creation:
May we strive to do your will.
You have made us as brothers and sisters with all that lives:
May we live together in peace.
A Reading: Job 38:4-7,18
‘Where were you when I laid the foundation of the earth?
Tell me, if you have understanding.
Who determined its measurements—surely you know!
Or who stretched the line upon it?
On what were its bases sunk,
or who laid its cornerstone
when the morning stars sang together
and all the heavenly beings shouted for joy?
Have you comprehended the expanse of the earth?
Declare, if you know all this.
During Lent I shall be focusing on the different continent; this week Antarctica.
Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent in terms of total area. There are no countries in Antarctica, although seven nations claim different parts of it: New Zealand, Australia, France, Norway, the United Kingdom, Chile, and Argentina. The Antarctic also includes island territories of South Orkney Islands, South Shetland Islands, South Georgia, the South Sandwich Islands, Peter I Island and Bouvet Island, Heard and McDonald islands, Scott Island and the Balleny Islands.
The Antarctic Ice Sheet dominates the region. It is the largest single piece of ice on Earth. This ice sheet even extends beyond the continent when snow and ice are at their most extreme.
Antarctica has a number of mountain summits, including the Transantarctic Mountains, which divide the continent into eastern and western regions. A few of these summits reach altitudes of more than 4,500m. The elevation of the Antarctic Ice Sheet itself is about 2,000m and reaches 4,000m above sea level near the centre of the continent.
The Antarctic region has an important role in global climate processes. It is an integral part of the Earth’s heat balance. The heat balance, also called the energy balance, is the relationship between the amount of solar heat absorbed by Earth’s atmosphere and the amount of heat reflected back into space.
Lichens, mosses, and terrestrial algae are among the few species of vegetation that grow in Antarctica. The interior has little if any vegetation. The ocean, however, teems with fish and other marine life – among the most diverse on the planet. Upwelling allows phytoplankton and algae to flourish. Thousands of species, such as krill, feed on the plankton. Fish and a large variety of marine mammals thrive in the cold Antarctic waters – especially blue, fin, humpback, right, minke, sei, and sperm whales. One of the apex predators in Antarctica is the leopard seal. The most familiar animal of Antarctica is probably the penguin. They have adapted to the cold, coastal waters. Their wings serve as flippers as they “fly” through the water in search of prey such as squid and fish. Their feathers retain a layer of air, helping them keep warm in the freezing water. https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/antarctica/
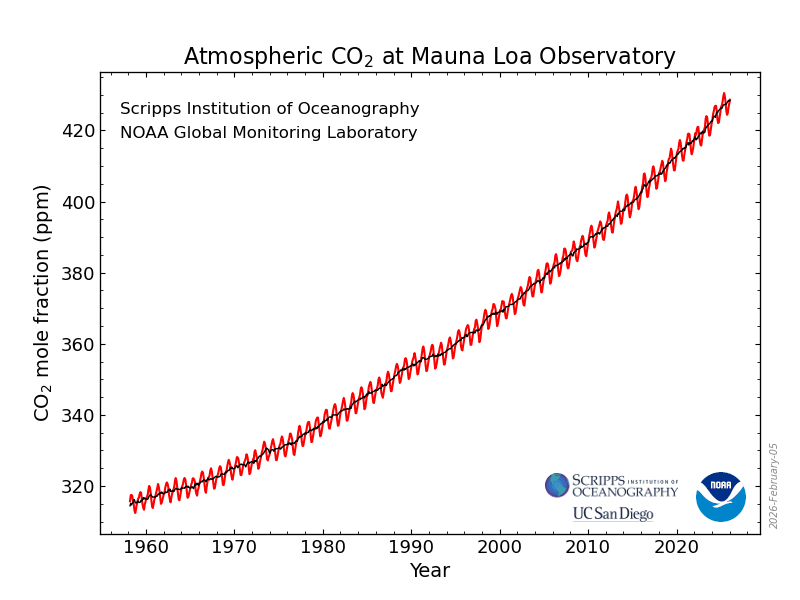
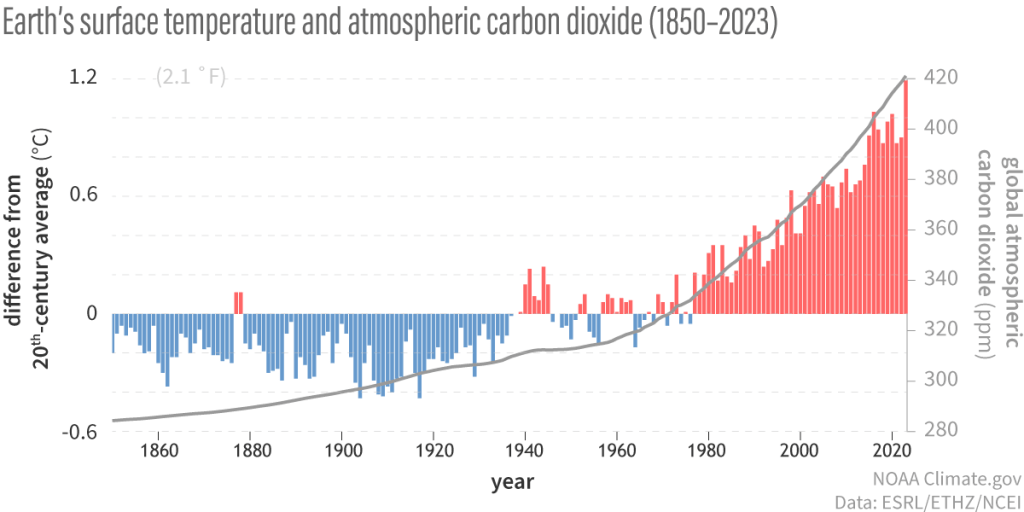
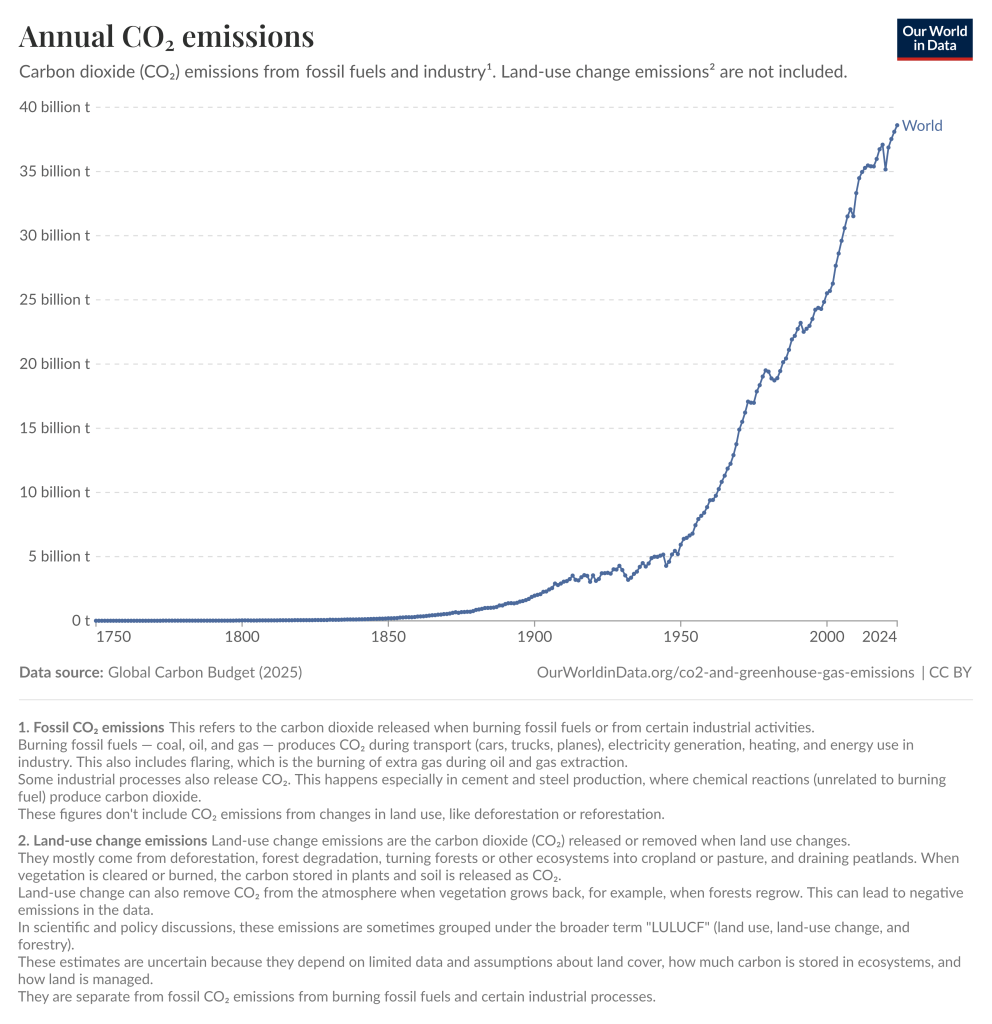
Global warming is raising temperatures and melting ice sheets. This has wide ranging impacts from rising sea levels, the disruption of ocean currents, the disruption of weather systems, the displacement of those living beings that only thrive in the particular Antarctic conditions and the consequential knock-on effect on other interdependent species.
Seeking first your kingdom & righteousness may all things needful be added to us.
We pray for the wellbeing of the Antarctic, the protection of its climate and preservation of its ice cap. Inspire and encourage us, as citizens and consumers, governments and leaders to truly address the means by which we can radically reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
You open your hand
and satisfy the desires of every living thing.
We recognise ourselves in the fractured and frail failures of the stories of God’s people. and we pause to reorient ourselves towards love of God and neighbour.
Love is patient; love is kind; love is not envious or boastful or arrogant or rude.
Our love has been as the morning mist, as the dew that goes early away.
God be gracious;
Lord, have mercy
Love does not insist on its own way; it is not irritable or resentful; Love does not rejoice in wrongdoing, but rejoices in the truth
Our love has been as the morning mist, as the dew that goes early away.
God be gracious;
Lord, have mercy
Love bears all things, believes all things, hopes all things, endures all things.
Our love has been as the morning mist, as the dew that goes early away.
God be gracious;
Lord, have mercy.
O Soul be joyful; our merciful God stretches out a loving hand to you.
(1 Cor 13:4-7; Hosea 13:3) https://ourcommonprayer.org/2017/07/22/lent/
The Grace